GraphQL subscriptions enable you to subscribe to events under a source stream and receive notifications in real time via a response stream when a selected event executes.
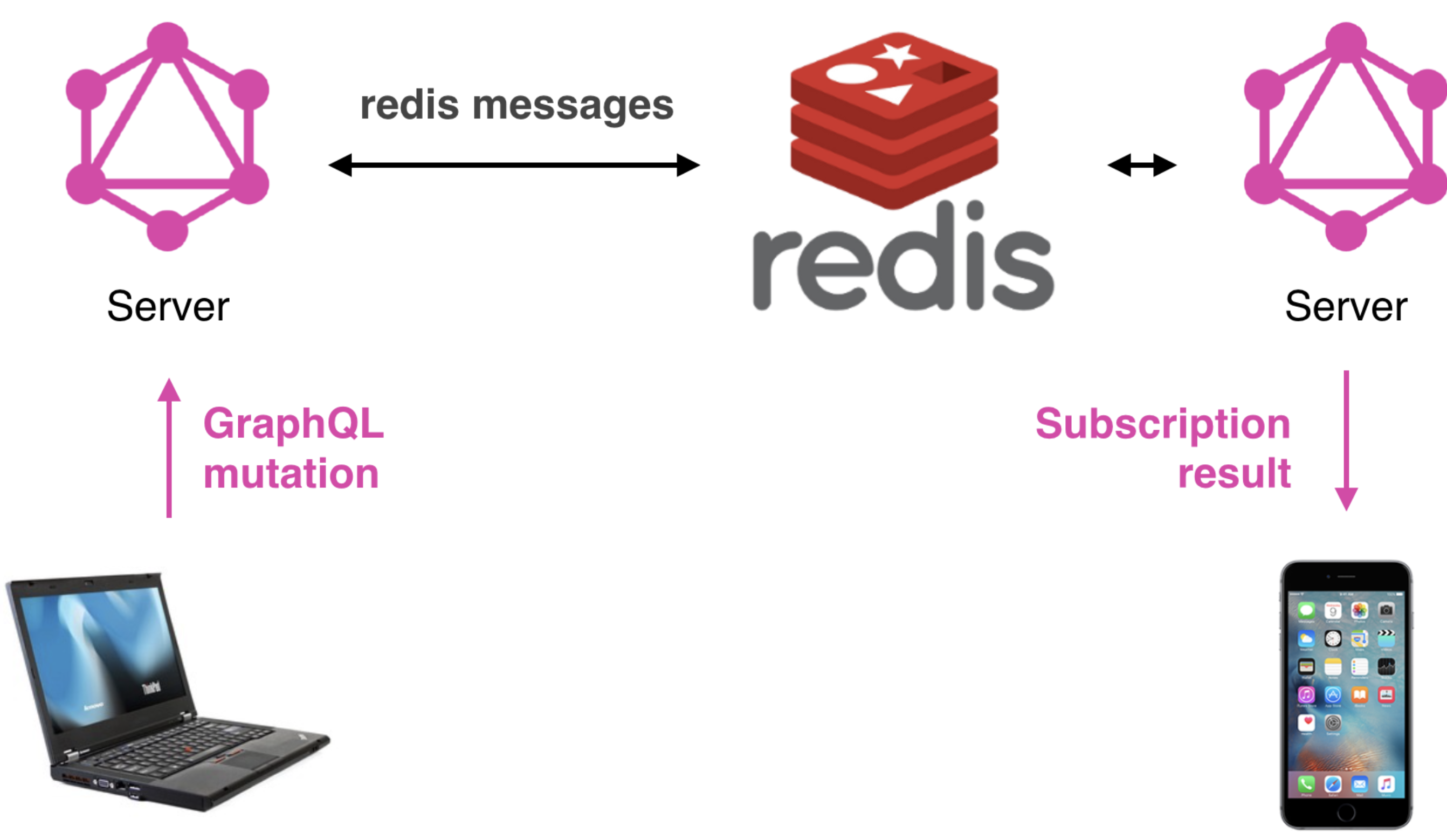
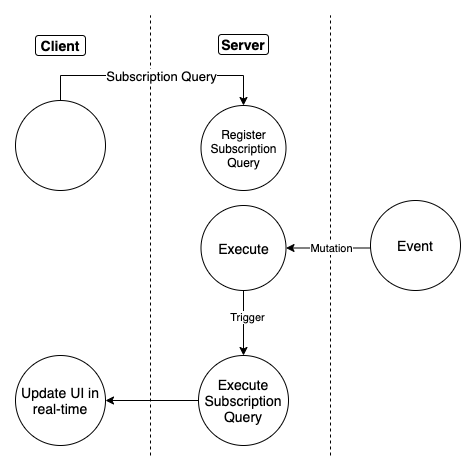
Once a GraphQL subscription is executed, a persistent function is created on the server that maps an underlying source stream to a returned response stream.
GraphQL subscriptions differ from queries in the way the data is delivered to the client.
Queries immediately returns a single response, while subscriptions return a result every time data is published on a topic the client has subscribed.
# Example: Hello Subscriptions
Below are the contents of the file index.js (opens new window) at repo crguezl/graphql-yoga-examples in the folder /subscriptions/hello-name.
import { GraphQLServer, PubSub } from 'graphql-yoga'
import { inspect } from 'util'
const ins = x => inspect(x, { depth: null})
const typeDefs = `
type Query {
hello(name: String!): String!
}
type Counter {
name: String!
count: Int!
countStr: String
}
type Subscription {
counter: Counter!
}
`
const resolvers = {
Query: {
hello: (parent, args, context) => {
const {pubsub, countMap} = context
const name = args.name;
let c = countMap.get(name) || 0;
countMap.set(name, ++c)
pubsub.publish("greetings", { counter: { name: name, count: countMap.get(name) }})
return `Hello ${name}`
},
},
Counter: {
countStr: (parent, args, context) => `parent: ${ins(parent)} args=${ins(args)}, context keys=${Object.keys(context)} countMap=${ins(context.countMap)}`,
},
Subscription: {
counter: {
subscribe: (parent, args, { pubsub, countMap }) => {
return pubsub.asyncIterator("greetings")
},
}
},
}
const countMap = new Map();
const pubsub = new PubSub()
const server = new GraphQLServer({ typeDefs, resolvers, context: { pubsub, countMap } })
server.start(() => console.log('Server is running on localhost:4000'))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# Running the example
We can run it with node index.js and see the output in the console:
➜ hello-name git:(main) ✗ node index.js
Server is running on localhost:4000
2
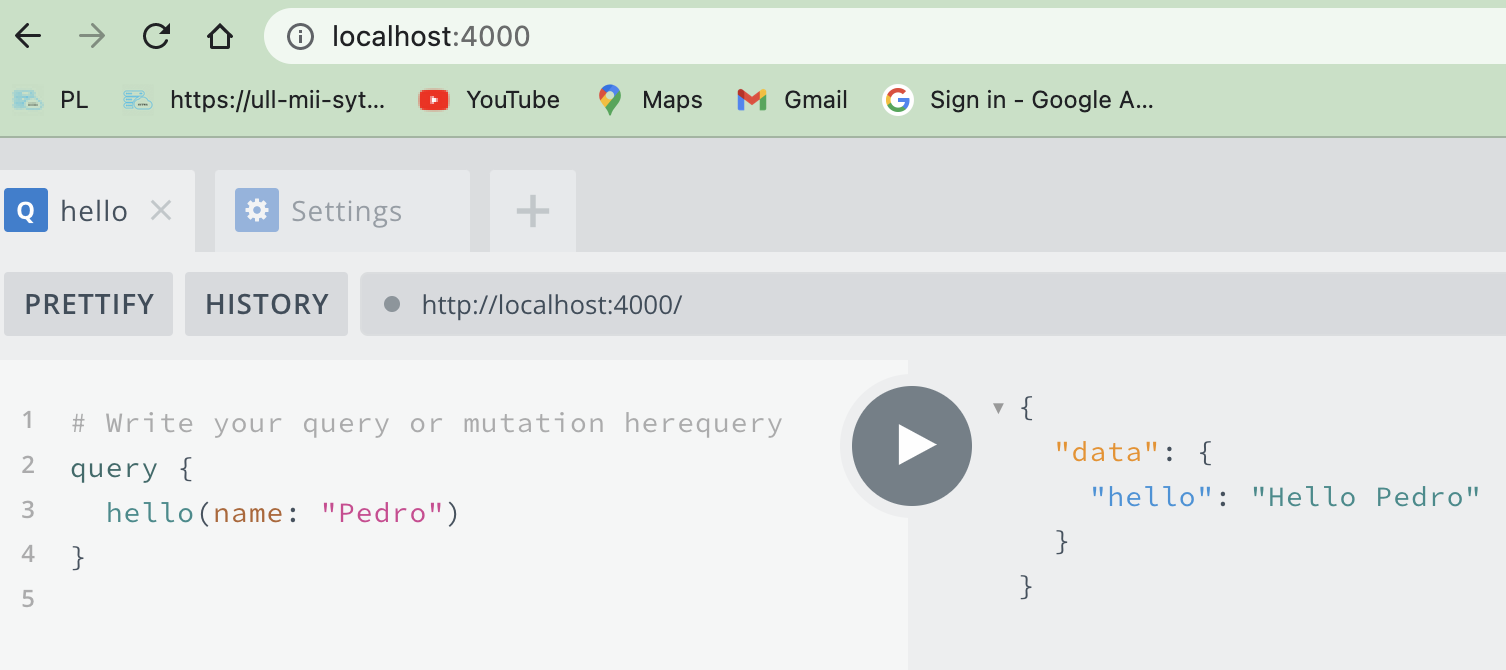
and then when we can open a couple of tabs on localhost:4000 and subscribe in one and make queries on the other. On the queries tab we make queries:
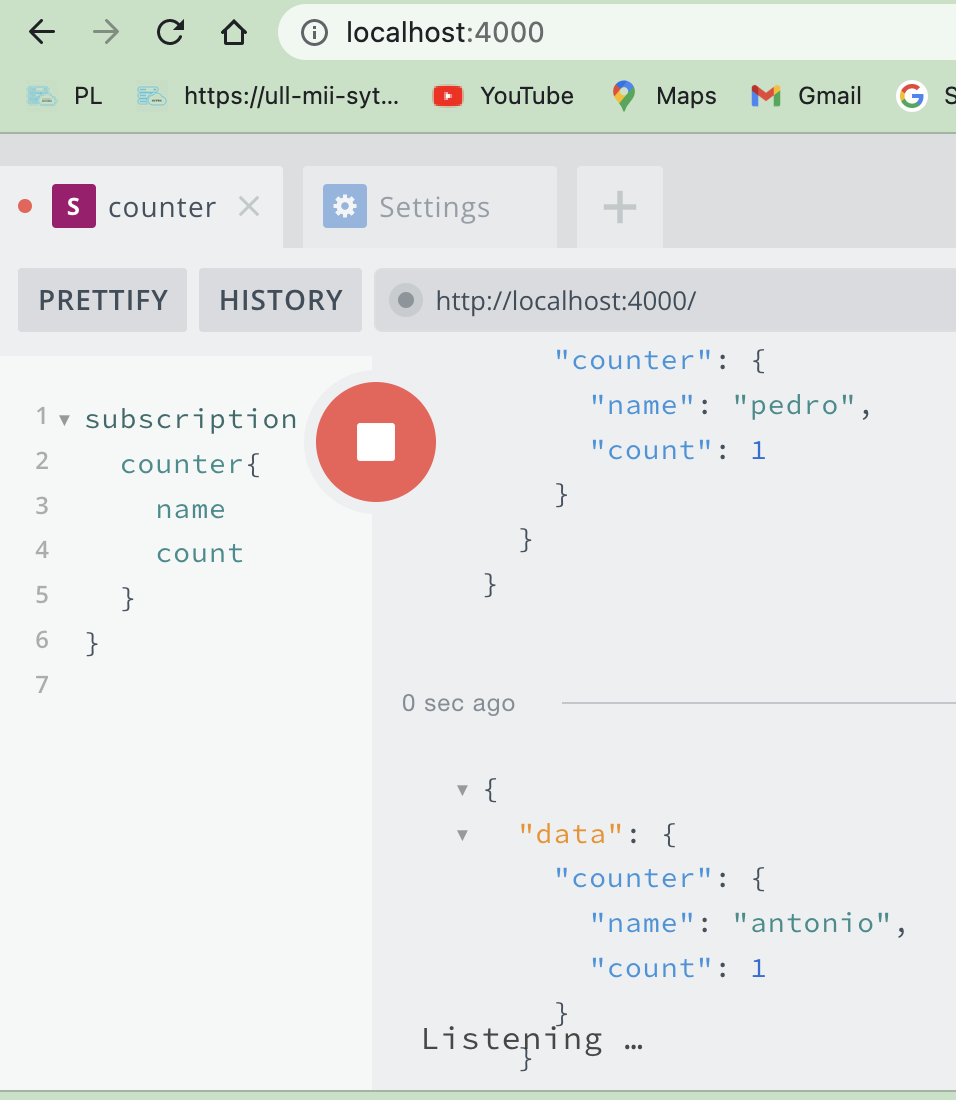
Once you are subscribed in the subscription tab, you can see the results :
# Explaining the code
A client can makes graphql queries to greet a specific person.
type Query {
hello(name: String!): String!
}
2
3
Each time a query is made, the server publishes a message to the channel greetings with the name of the person greeted and the number of times she has been greeted:
const resolvers = {
Query: {
hello: (parent, args, context) => {
const {pubsub, countMap} = context
const name = args.name;
let c = countMap.get(name) || 0;
countMap.set(name, ++c)
pubsub.publish("greetings", { counter: { name: name, count: countMap.get(name) }})
return `Hello ${name}`
},
},
/* ... */
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
clients subscribed to the channel greetings will receive the message and will be able to see the number of times the person has been greeted.
On the main code we start by creating the Map and the PubSub instances:
const countMap = new Map();
const pubsub = new PubSub()
const server = new GraphQLServer({ typeDefs, resolvers, context: { pubsub, countMap } })
server.start(() => console.log('Server is running on localhost:4000'))
2
3
4
5
The line const pubsub = new PubSub() creates
a simple PubSub instance - it is a simple pubsub implementation, based on EventEmitter.
Alternative EventEmitter implementations can be passed by an options object to the PubSub constructor.
PubSub (opens new window) is a class that exposes a simple publish and subscribe API. It provides a basic in-memory event bus to help you get started.
As you can see at the line:
PubSub (opens new window) sits between your application's logic and the GraphQL subscriptions engine - it receives a publish command from your app logic and pushes it to your GraphQL execution engine.
pubsub.publish("greetings", { counter: { name: name, count: countMap.get(name) }})
Notice how we pass the pubsub and countMap instances to the context of the GraphQLServer:
const server = new GraphQLServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
context: { pubsub, countMap }
})
2
3
4
5
# References
- See folder
subscriptions/hello/ in the repocrguezl/graphql-yoga-examples` (opens new window) - apollographql documentation: subscriptions (opens new window)
- GraphQL subscriptions with Node.js and Express (opens new window) by https://blog.logrocket.com/graphql-subscriptions-nodejs-express/) by Deepak Gupta, November 11, 2021
- Tutorial (opens new window) Building live chat app with GraphQL subscriptions
- apollographql/graphql-subscriptions (opens new window)
- Realtime GraphQL Subscriptions (opens new window) from GRAPHQL-NODE TUTORIAL. Written by Maira Bello: Build your own GraphQL server